SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are complex collections of RTUs, PLCs, sensors and actuators that together are utilized to monitor and manipulate industrial processes. In short, SCADA systems collect real time data and process the data in order for operators to interact with it. There is also a software aspect in SCADA applications which provides operators with a framework and means to access and control SCADA hardware components.
SCADA systems have a wide range of applicable processes including both automated processes and analytical capacities for remote/local data gathering.
Hardware components such as RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) are field devices used extensively in SCADA systems in order to collect data from sensors and relay it to the SCADA software. PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) however are industrial devices which control machinery and are in constant communication with the SCADA software. RTUs and PLCs both play distinct roles in the performance of a SCADA system however. The SCADA software is the binding component that creates a comprehensive system. Data gathered from this communication is then processed by the SCADA software into a useable and readable display for users to interact and analyse.

SCADA Software
As the global economy and technology sector becomes more mechanised and directed by units and devices, software to control it becomes more necessary and prevalent every day. MatDeck SCADA is a SCADA software forms that provides operators with a simple visual interface for supervisory control systems for procedures such as:
- Monitor the state of the system and its performance
- Control processes remotely
- Log historical data
MD SCADA also provides operators with the ability to log and monitor data from Excel files and/or databases.
MatDeck SCADA
- Easy to use Drag and Drop No Code SCADA
- Utilize Python code directly with MD SCADA form
- Advanced Python SCADA with coding in Python or MD Script
- No Code GUI Toolboxes for DAQ Configuration and Commutation, PID, FFT, DSP as well as Signal Generating and Curve Fitting GUI Toolboxes
- Database toolboxes with SQLite already installed. User can use other databases
- AI Functions and Forms for modelling
- Drag and Drop ready-made Instruments for Python SCADA and No Code SCADA plus all features below are for Python SCADA and No Code SCADA.
- Functions for DSP, Data Acquisition, Signals, Vibration, PID and Wavelets
- Various Advantech, ICP DAS, LabJack and other devices
- Array Fire GPU acceleration
Codeless drag and drop SCADA
Similar to MatDeck’s Virtument, MD SCADA’s framework is designed to reduce time spent on design and configuration. Essentially, MatDeck is responsible for processes such as sending/receiving data, logging and displaying data meaning operators can instead create professional SCADA terminals in minutes.
As with most MatDeck features, our SCADA can be manipulated and used with other MatDeck features. This means SCADA and other features (Graphs, Math functions, Programming…) can be used together in the same MD documents.

SCADA and Python
Python as a stand-alone programming language is known for its easy to sue syntax and flexibility. These features are what make Python a viable and perfect option to be used with MD SCADA. Being able to directly communicate with MD SCADA, users can bring countless Python libraries and years of preexisting code. As all interactable widgets and visual SCADA features are deployed through drag and drop, operators will only code for functionality specific to their needs. For simple SCADA control, supervisory layer can be utilized in Python.
Dedicated Simple SCADA Panels
While configuration forms are vital to set up your SCADA applications, SCADA applications wouldn’t exist without SCADA panels. Here, you can add, remove and edit various SCADA individual SCADA elements.
MatDeck SCADA panels are similar to Virtument panels in MatDeck and use a simple window that contains the work area and various elements that can be deployed.
Each individual SCADA element is equipped with an advanced degree of customisation. Paired with this, most SCADA elements contain their own unique settings specific to that element’s aesthetics and function. Elements can be changed and altered according to the user’s needs and aims.
While each element can possess their own unique settings, all element’s include aesthetic and data channel properties that can be customised.
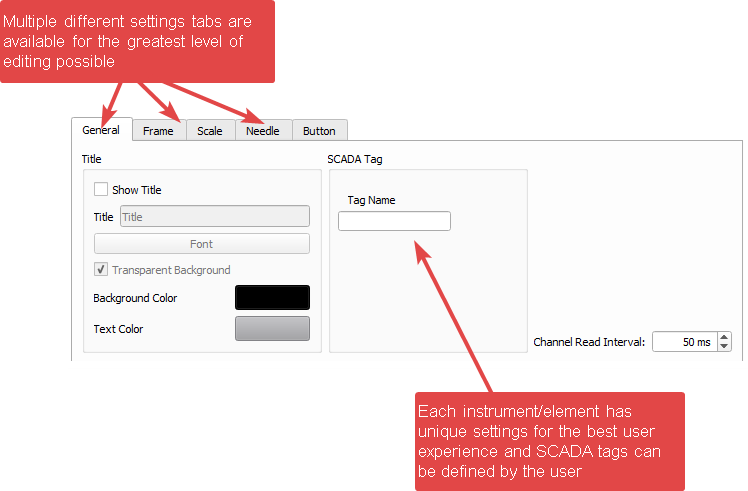
As shown below, MD SCADA panels utilise a similar and familiar design to MatDeck’s virtual instrumentation toolbox, Virtument, where a main work area composes most of the panel. Here, operators can simply drag and drop elements from the sidebar on the right. The instrument sidebar contains 18 individual instruments that can be placed drag and drop on the main work area. The main SCADA work area can contain over 30 individual instruments at any given moment.

Similar to the configuration forms, SCADA panels can be used and embedded within a MD document or as a standalone window.
Utilising the various settings and functions available in the MD SCADA panel together will allow operators to represent data accurately and efficiently. Above is an example of how the various elements can be used to create a SCADA application in MatDeck.
SCADA configuration forms in Python SCADA and Codeless SCADA
SCADA applications are comprised of two main layers:
- Devices and units used to send, control and receive data
- Software used to interpret and display data for operator use
The device and unit aspect of SCADA system is extensively present on the machine side of industrial processes and necessary to actuate the changes and commands the operator performs. The software aspect however is on the operator side of SCADA systems detailing and facilitating operators with a means to interpret and act upon data collected on the machine side. This means communication between the device unit and the SCADA application is essential.
Custom manufacturer dedicated MatDeck SCADA configuration forms allow for hundreds of devices to be connected and configured. Depending on the manufacturer, different configuration forms are available for different devices.
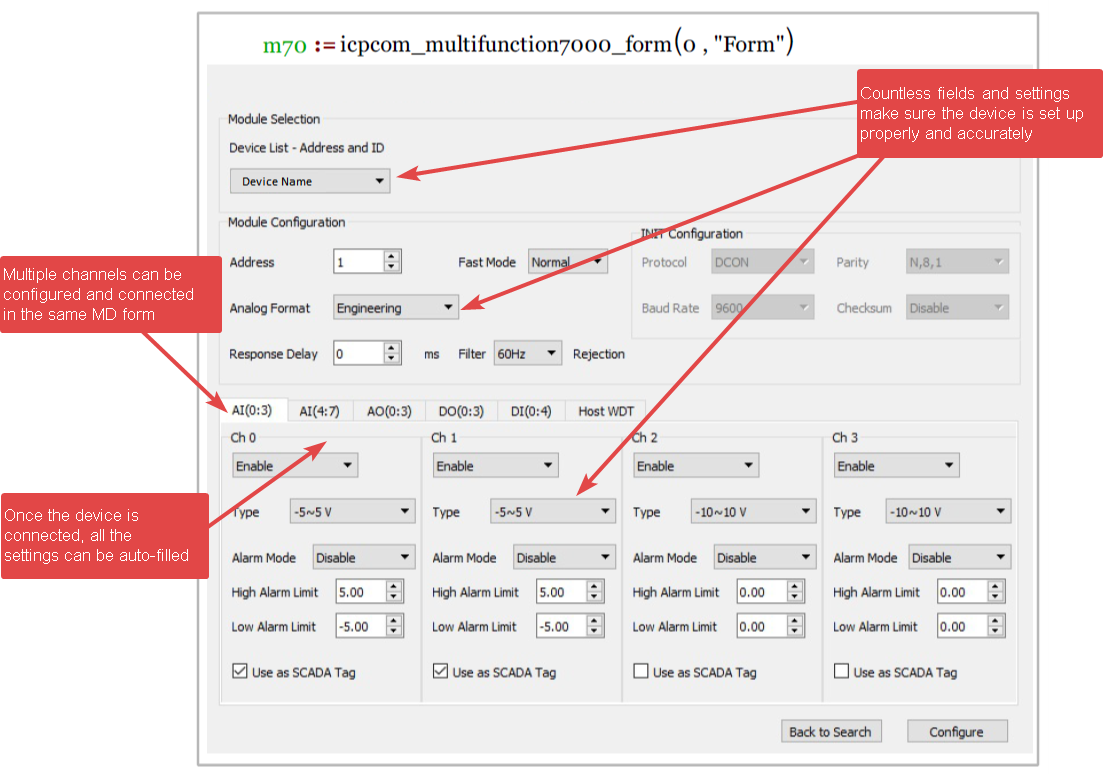
With the device configuration form, the SCADA configuration form is used.
This SCADA configuration form is used to connect specific SCADA hardware data inputs/outputs to specific channels. As can be seen in the example form above, specific settings such as the Alarm mode, min/max values, and sampling rate can be set to the operator’s needs for each specific SCADA element.
MatDeck maintains its universal framework even when dealing with SCADA applications. Both the unit device and SCADA configuration forms can be used and manipulated in the same document.
Single MatDeck documents can house all necessary functions and features of SCADA application so editing and maintenance is made as simple as possible. Not to mention, other MD features can be used and mixed with the SCADA eliminating the need for other software and complex procedures.
Simple SCADA forms and databases
As mentioned above, MatDeck allows you to log your data to various databases. To accommodate for different operators with different database needs, SQLite is already installed in MatDeck and ready in order to save time and simplify recording SCADA data. MatDeck SCADA panels can directly connect to database and SQLite. Using the simple SCADA form is a more efficient method for data to be monitored, controlled, processed, logged and represented within the panel.
MatDeck GUI Designer for SCADA

Virtument for SCADA
Virtument’s drag and drop virtual instrument panel simplifies the process without a need for coding with Python and MD script. It is used as a HDI interface in conjunction with SCADA Forms and SCADA data channels.

SCADA HMI – Human Machine Interface
HMIs are the part of the SCADA system that are most interacted with and seen by users. HMIs refer to the actual visual representation made by the software for users to actualise the often-large scale works and allows them to monitor data and interact with RTUs and PLCs. HMIs need to be efficient and intuitive in the way they allow users to understand the system as time is a sensitive aspect in SCADA. Making sure users can quickly understand and process what’s occurring in the system is a theme that is achieved intuitively by MD SCADA. By having a diverse vault of graphical representations and diagrams, users can simply design and draw their industrial processes in MD SCADA and in a time sensitive environment be the first to understand what is occurring in their works.
Equipped with each various option for their diagram, each applicable widget has a deep level of customization available so even users working on single PCs can tailor their SCADA system for themselves. By taking advantage of the straightforward HMI present in MD SCADA panels, users with little experience can become up to date with their system extremely quickly.
SCADA applications features
SCADA applications can vary greatly and apply to a large variety of processes however, specific features are often similar or even the same across different SCADA applications. Key advantages of SCADA such as retrieving and representing complex data from sensors, control over processes both remotely and automatically, reducing supervision costs and downtime should all be exploited to the maximum in order to increase the utility of each industrial or small-scale process. Processes that align with SCADA’s advantages tend to be manufacturing or large processes where hardware units and sensors are deployed across a large spread.
SCADA Supervisory Controller
Supervisory Controllers, alternatively known as an MTU (Master Terminal Unit), take the form of the main interaction between the hardware and software working together in SCADA systems. Located in the control centre of the industrial process, MTUs manage and control the communication between HMIs and RTUs. Large SCADA systems will naturally have larger Supervisory Controllers made of several servers and dedicated maintenance teams. MatDeck can be both applied to larger scale systems as well as SCADA configurations on single computers.
SCADA Control RTUs and PLCs
While Remote Telemetry Units (RTU) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) serve similar purposes within the SCADA system, both have important and stark differences. One commonality is both can be interpreted and connected to MatDeck software solutions so information and data gathered by them can be processes and displayed synchronously. However, where RTUs and PLCs differ is in design and individual capability. RTUs are designed for remote use with static purposes and features meant to be reliable but hard to change. PLCs on the other hand, are designed for local use due to their more dynamic nature being able to be reprogrammed and utilizing wired connections instead of wireless compared to RTUs.
Both can be easily equipped with MatDeck SCADA and the user’s preference will often determine which one is better suited for their process/application. PLCs also tend to be smaller so naturally, with a lower number of I/O ports will be better suited for smaller applications.
Examples of this include
- Manufacturing and production – Here SCADA systems can perform round the clock monitoring of industrial automation and devices. Paired with this, it provides manufacturers a more full-proof method of controlling and recording data relevant to the process.
- Centralised control and monitoring of buildings – Buildings will tend to have various facets of device and access spread across numerous floors and rooms. SCADA systems provide a centralised solution where management can view and control entire building functions from one HMI.
- Traffic signals – Another example of an incredibly large and spread-out system where being able to monitor and control each node (Traffic Light) is crucial. Users can encode specific fail safes and controls in MatDeck to detect erroneous signals and correct them before larger aftereffects can occur.
- Telecommunications – This exemplifies SCADA system’s important ability to control and monitor remotely where having SCADA systems at each point within a system is simply not feasible and too expensive.
SCADA FAQ
How do I use SCADA in MatDeck?
Using SCADA in MatDeck requires 3 main steps. First, you need to initialise the correct MD SCADA configuration form and configure the data channels to your needs. Once done, create your visual SCADA design using the virtual instrumentation within Virtument. Now, using either Python or MD script you can start to code your system control and how your application will interact with the data channels.
Does MD have signal condition and FFT?
MatDeck has various functions for signal conditioning, averaging, filtering, and FFT. MatDeck has approximately 2000 functions.
What is MD’s data acquisition?
MatDeck can be connected to numerous hardware devices where you can perform various measurements and high quality data acquisition. Data can be saved in Excel files or specific databases.
How do you use Python in SCADA?
Similar to the question, How do I use SCADA in MatDeck?, Python code can be deployed and coded in both standard MD documents or dedicated script files. Here, Python code can directly interact and manipulate data that is sent and received by the SCADA’s data channels.
Why is SQLite installed in MatDeck?
Traditionally, database systems would need to be interfaced with the SCADA system. With MatDeck, the necessary database system is already installed in MatDeck and ready to use. Naturally, for users who wish to use an alternative to SQLite, other database systems can be connected and installed.
How much does MatDeck cost?
MatDeck year subscription is priced at £340.00 and a perpetual license is priced at £692.00. The main approach to all MatDeck software and additions is to be affordable and accessible to both novice and experienced users.
How do you use MD functions?
MatDeck is equipped with approximately 2000 different functions that vary across multiple industries and fields. Each class of functions has ready-made examples and instructions on our website. These can be found at https://labdeck.com/help/
